MORE THAN 70% of global polyethylene demand is at risk from ageing populations, climate change and geopolitics.
Asian Chemical Connections
Petrochemicals after the Supercycle: Revised scenarios
LET ME AGAIN bang away on the same old drum which I’ve covered with a new skin: The above slide is an updated version of the slide I first published late last year. Note that there is a new scenario added to the original two, A Bi-polar World. Also note that I have this time included percentage weightings of my views on the likelihoods of the scenarios.
China’s petrochemicals capacity growth: A new normal of much greater uncertainty
UNDERSTANDING what was going to happen next with petrochemicals capacity additions in China used to be easy. Now we are in a world of muddle and ambiguity.
Supermajors versus Deglobalisation scenarios: The impact on petrochemicals and recycling
THERE ARE TWO scenarios or roads down which the petrochemicals industry could travel over the next ten years, with arrival either at Supermajors or Deglobalisation.
Details of how Saudi Aramco COTC and other advantaged feedstock projects could redraw the petrochemicals map
There is a big new wave of lower-carbon and very advantaged cracker projects on the way, including Saudi Aramco’s crude-oil-to-chemicals investments.
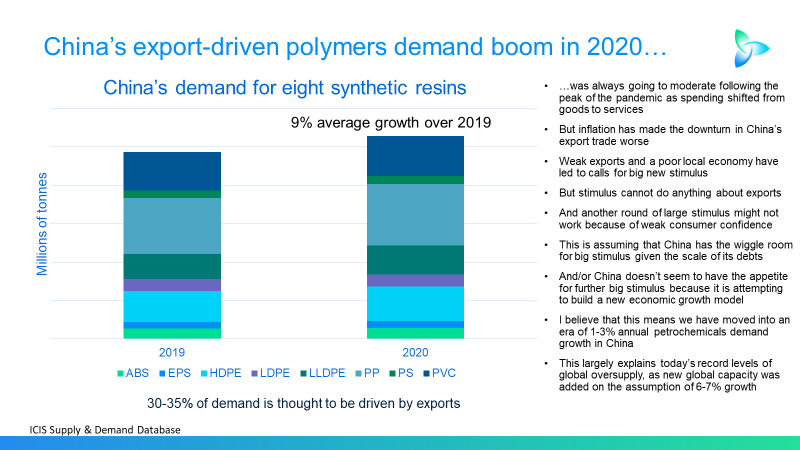
China and “pushing on a piece of string: The moderate impact of future economic stimulus
THE PHRASE “pushing on a piece of string” might best describe the logic behind calls for another round of big economic stimulus in China. Any extra money pumped into the economy could be largely saved rather than spent because of weak consumer confidence resulting from an ageing population and the end of the property bubble.
The old China and HDPE, the new China and the future of demand
In my downside scenario for China’s HDPE demand in 2023-2040 is correct, the country’s total consumption during this period would be 134m tonnes lower than the ICIS Base Case.
Competing voices and the chemicals challenge of cutting carbon
We don’t have much time. We must act quickly to prevent potentially catastrophic social, political and economic damage from climate change.
India, climate change, demographics and polymers demand growth
Climate change and demographics are economic destiny – their effects cannot be avoided. But the petrochemicals industry has a huge role to play in shaping favourable outcomes
Why European chemicals can emerge from this crisis as a winner
IT REALLY ISN’T doom and gloom if you take the longer-term view. Instead, for the chemical companies with the right strategies, the opportunities to build new sustainable business models are huge. The winners will make an awful lot of money while also doing the right things for humanity and our natural environment.